Covalent Bounding
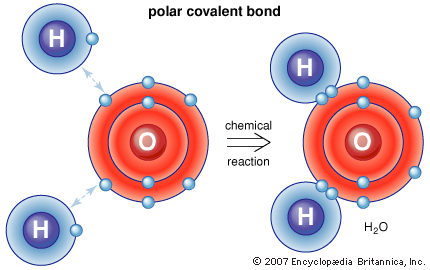
In a Polar Covalent Bond the sharing of the electron par is unequal. When the electrons are spending more time around the
nonmetallic atom thats when it forms a polar covalent bound. The ability of an atom to attract electrons in the presense of
another atom is a measurable property called electronegativity. The result of this pattern of unequal electron assocition is a
charge separation in the molecule, where one part of the molecule, the oxygen, has a parital negative charge and the
Hydrogen have a partial postive charge.
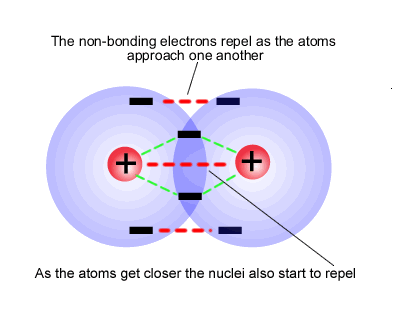
Covalent bonds are forces that hold together. Some of the forces are formed when the atoms of a molecule share electrons.
1)Having covalent bonds representing a chemical potential energy that can be used is
boilogical reactions.
2)The angles formed between covalently bonded atoms are specific and defined. This
meas that biological molecules formed with covalent bonds have definite and predicable
shapes.
3) In biological systems, covalent bonds are called strong bonds. This means that they are
not normally broken under
biological conditions unless by enzymic catalysis. This is in opposition to weak bonds like
hydrogen and ionic bonds which are easily broken under normal boilogical conditions
temperature and pressure.
4) In biological systems, covalent bonds are called strong bonds. This means that they are
not normal biological conditions unless by enzymic catalysis.